Check those Symptoms – Do You Have a Vitamin Deficiency?
Prevent nutrient deficiencies after surgery by meeting protein goals, eating a variety of healthy foods, taking vitamin and mineral supplements and having labs monitored every 3 months for the first year after surgery and then annually. Contact your nutritionist or surgeon with questions.
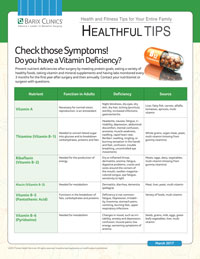
| Nutrient | Function in Adults | Deficiency | Source |
| Vitamin A | Necessary for normal vision, reproduction, is an antioxidant | Night blindness, dry eyes, dry skin, dry hair, itching (pruritus), sterility, increased infections, gastroenteritis | Liver, fatty fish, carrots, alfalfa, tomatoes, apricots, multi vitamin |
| Thiamine (Vitamin B-1) | Needed to convert blood sugar into glucose and to breakdown carbohydrates, proteins and fats | Headache, nausea, fatigue, irritability, depression, abdominal discomfort, mental confusion, anorexia, muscle weakness, swelling, rapid heart rate, Beriberi: swelling, tingling, or burning sensation in the hands and feet, confusion, trouble breathing, uncontrolled eye movements
| Whole grains, organ meat, yeast, multi vitamin (missing from gummy vitamins) |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B-2) | Needed for the production of energy | Dry or inflamed throat, dermatitis, anemia, fatigue, digestive problems, cracks and sores around the corners of the mouth, swollen magenta-colored tongue, eye fatigue, sensitivity to light | Meats, eggs, dairy, vegetables, multi vitamin (missing from gummy vitamins) |
| Niacin (Vitamin B-3) | Needed for metabolism | Dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia (pellagra) | Meat, liver, yeast, multi vitamin |
| Vitamin B-5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Functions in the breakdown of fats, carbohydrates and proteins | Deficiency is not common: fatigue, Depression, Irritability, Insomnia, stomach pains, vomiting, burning feet, upper respiratory infections
| Found in a wide variety of foods, multi vitamin |
| Vitamin B-6 (Pyridoxine) | Needed for metabolism | Changes in mood, such as irritability, anxiety and depression; confusion; muscle pains; low energy; worsening symptoms of anemia | Seeds, grains, milk, eggs, green leafy vegetables, liver, multi vitamin |
| Folic Acid (Vitamin B-9) | Necessary for normal cell division | Anemia (megaloblastic) Poor growth, tongue inflammation, gingivitis, loss of appetite, shortness of breath, diarrhea, irritability,forgetfulness.
| Meat, liver, eggs, leafy vegetables, multi vitamin |
| Biotin | Needed in the metabolism of protein, fats and carbohydrates | Hair loss (alopecia), a scaly red rash around the eyes, nose, mouth, and genital area, cracking in the corners of the mouth (cheilitis), swollen and painful magenta colored tongue (glossitis), dry eyes, fatigue, insomnia, depression | Bacteria in the intestines produce biotin, eggs, meat, nuts, milk, grains, multi vitamin |
| Vitamin B-12 (Cyanocobalamin) | Needed for DNA synthesis, protein metabolism, proper nerve function | Anemia (pernicious): weakness, tiredness, lightheadedness, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, pale skin; a smooth tongue, constipation, diarrhea, loss of appetite, nerve problems: numbness or tingling, muscle weakness, and problems walking; vision loss, mental problems: depression, memory loss, or behavioral changes
| Animal sources like meat, milk, eggs After weight loss surgery vitamin B-12 isn’t absorbed well in the digestive system and sublingual (under the tongue) supplements or injections may be needed |
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | Needed for wound healing, improves immune function | Tiredness, weakness, muscle and joint pains, easy bruising, spots that look like tiny, red-blue bruises on your skin, dry skin, splitting hair, swelling and discoloration of your gums, sudden and unexpected bleeding from your gums, nosebleeds, poor healing of wounds, problems fighting infections, joint pains, changes in your bones, tooth loss
| Found in citrus fruits, berries, melon, tomatoes, green peppers and cabbage |
| Vitamin D | Maintains healthy levels of calcium and phosphorus in the body. | Rickets (a disease in which the bone tissue doesn’t properly mineralize, leading to soft bones and skeletal deformities), osteoporosis, increased risk of death: from heart disease, cognitive impairment in older adults, and cancer
| Fish, fish liver oils, and egg yolks — and in fortified dairy and grain products. |
| Vitamin E | Important antioxidant, essential for fat metabolism, reproduction | Lipid metabolism disorders, anemia (hemolytic), infertility, increased risk of heart disease or cancer, muscle weakness, loss of muscle mass, abnormal eye movements, vision problems, unsteady walking, long-term deficiency may also cause liver and kidney problems
| Vegetable oils, seeds, nuts, fruits and vegetables |
| Vitamin K | Key role in blood clotting and bone health | Deficiencies are rare but could result in excessive bleeding or osteoporosis | Produced by bacteria in the gut, beef liver, green tea, turnip greens, broccoli, kale, spinach, cabbage, asparagus, and dark green lettuce |
Download Healthful Tips: Check those Symptoms–Do you have a Vitamin Deficiency?